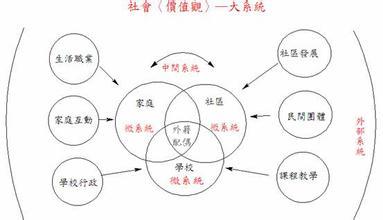
生态系统的理论
的有关信息介绍如下:1935年,英国生态学家,亚瑟·乔治·坦斯利爵士(Sir Arthur George Tansley)受丹麦植物学家尤金纽斯·瓦尔明(Eugenius Warming)的影响,明确提出生态系统的概念。认为:
“(原文)But the fundmental conception is, as it seems to me, the whole system (in the sense of physics), including not only the organism-complex, but also the while complex of physical factors forming what we call the enviriment, with which they form one physical system. ... These ecosystems, as we may call them, are of the most various kinds and sizes. They form one category of the multitudinous physical systems of the universe, which range from the universe as a whole down to the atom. (Tansley A G. The use and abuse of vegetational concepts and terms. Ecology, 1935,16(3):284-307.P 299)”(但是对我来讲,基础概念是整个系统(从物理学中的意义来说),包括了有机体的复杂组成,以及我们称之为环境的物理要素的复杂组成,以这些复杂组成共同形成一个物理的系统。... 我们可以称其为生态系统,这些生态系统具有最为多种的种类和大小。他们形成了宇宙中多种多样的物理系统中的一种类型,而物理系统从宇宙整体到原子的范围。)
坦斯利对生态系统的组成进行了深入的考察,为生态系统下了精确的定义。
1940年,美国生态学家R.L.林德曼(R.L.Lindeman)在对赛达伯格湖(Cedar Bog Lake)进行定量分析后发现了生态系统在能量流动上的基本特点:
·能量在生态系统中的传递不可逆转
·能量传递的过程中逐级递减,传递率为10%~20%
这也就是著名的林德曼定律。